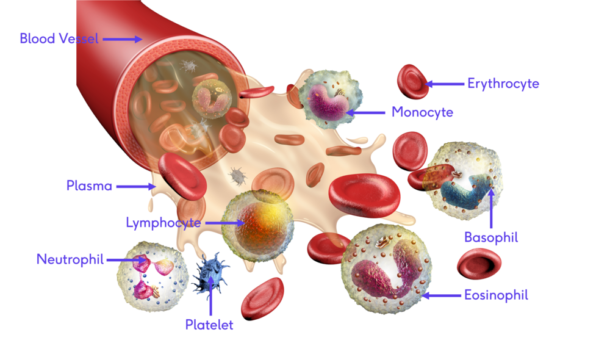
What is Hematology?
Hematology is a branch of medicine concerning the study of blood, the blood-forming organs, and blood diseases. The word "heme" comes from the Greek for blood.
Scope of hematology
Hematology is practised by specialists in the field who deal with the diagnosis, treatment and overall management of people with blood disorders ranging from anemia to blood cancer.
Disorders related to hematology
Various disorders and diseases primarily affect the blood and may be studied and treated by a hematologist. Some examples include:
- Anemia: This involves the body producing too few healthy red blood cells to carry enough oxygen around the body.
- Sickle cell disease: This form of anemia changes the shape of red blood cells.
- Thalassemia: This involves the body not making enough hemoglobin.
- Bleeding disorders: These prevent the body from forming blood clots correctly.
- Thrombocytopenia: This involves a low platelet count, which can result in difficulty forming blood clots.
- Malaria: This infection can destroy red blood cells.
- Von Willebrand’s disease: This bleeding disorder occurs in people who do not have a blood protein called von Willebrand factor.
- Thrombosis: This refers to a clot in a blood vessel.
- Hypercoagulability: This describes the blood’s increased tendency to clot.
- Blood cancers: These can affect the function of a person’s blood cells.
Hematology tests
Tests and procedures that a hematologist may perform include:
- Complete blood cell count: This test can help diagnose anemia, inflammatory diseases, and blood cancer. It can also help with monitoring blood loss and infection.
- Platelet count: This test helps diagnose and monitor bleeding disorders.
- Blood enzyme tests: There are many types of these tests, which a doctor uses to help diagnose cardiovascular conditions, including heart attack.
- Bone marrow biopsy: This procedure can help diagnose and monitor anemia, thrombocytopenia, which involves having a low platelet count, and some cancers.
- Blood transfusions: It involves the body receiving healthy blood intravenously through an IV.
Other hematology tests include:
- blood chemistry test
- blood enzyme test
- blood tests to assess heart disease risk
Treatments by Hematologists
- Iron deficiency anemia and other types of anemia such as sickle cell anemia or trauma-related anemia
- Polycythemia or excess production of red blood cells
- Myelofibrosis
- Leukemia
- Platelet and bleeding disorders
- The myelodysplastic syndromes
- Hemoglobinopathies such as thalassemia and sickle cell disease
- Multiple myeloma
- Malignant lymphomas
- Blood transfusion
- Bone marrow stem cell transplantation

 WhatsApp
WhatsApp